Understanding Architectural Diagrams: 15 types explained with examples.
Introduction
Architectural diagrams are schematic representations of the design process used by architects to explore design possibilities and illustrate design development to stakeholders.
The main differences between architectural diagrams and architectural drawings.
Architectural diagrams are schematic and used to visualise design development. Commonly used to illustrate spatial qualities, circulation and movement and structural strategies.
Architectural drawings are a direct representation of an architectural proposal. Used in the final stages of the design process to outline direct design and use intent.
Importance of Architecture Diagrams in Design and Presentation.
Architectural diagrams allow architects to explore design considerations quickly without producing detailed architectural drawings.
Architectural diagrams are crucial to facilitate communication among stakeholders.
Architectural diagrams aid in design development and decision-making and record a visual roadmap for your entire architectural project.
By understanding architectural diagrams, you will have the ability to explore all design considerations and illustrate them clearly through various diagrammatic formats.
We have created this guide in ‘Understanding Architectural Diagrams’ and explained 15 types to help you elevate your design skills.
Scroll to the bottom to download our Architecture Diagrams Checklist PDF for FREE
Summary of Understanding Architectural Diagrams.
-
Planimetric Architectural Diagram (Plans)
Sectional Architectural Diagrams
Axonometric Architectural Diagram
Isometric Architectural Diagram
Exploded Axonometric / Isometric Architectural Diagram
Programmatic Architectural Diagram
Contextual Architectural Diagram
Architectural Circulation Diagrams
Structural Architectural Diagram
Scaled Architectural Diagram
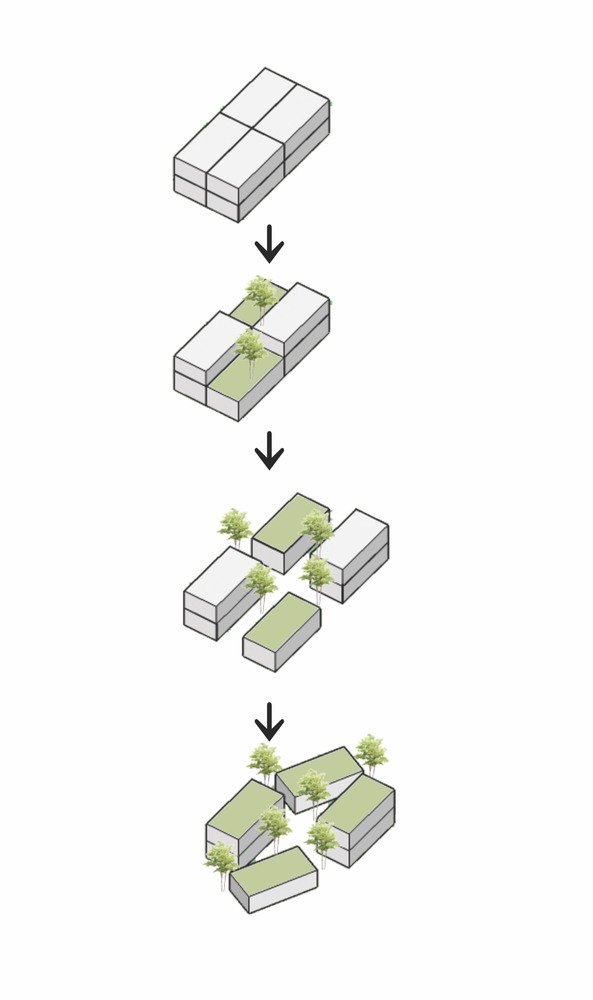
Design Development Architectural Diagram
Building Phases Architectural Diagram
AI Generative Architectural Diagram
Spatial Architectural Diagram
Volumetric Architectural Diagrams
Types of Architecture Diagrams
1. Planimetric Architectural Diagram (Plans)
1.1 What are Planimetric Diagrams
Planimetric diagrams, including floor plans, site plans, location plans master plans. Which are created from a bird's-eye view of a building or space and its context.
A planimetric diagram can detail the arrangement of rooms, spaces, contextual relationships etc. created from a top-down 2D horizontal plane.
1.2 Use Cases for Planimetric Diagrams
Planimetric diagrams are used by architects to strategise the layout of a project’s spaces, ensuring optimum functionality and flow within the proposal.
During the design development stage, they are used to explore circulation, spatial relationships, and orientation across a variety of scales.
1.3 Advantages and Considerations of Planimetric Diagrams
The simplicity of planimetric diagrams makes them an effective tool for initial design development and discussions. A refined planimetric diagram can provide clear design intentions to stakeholders.
2. Sectional Architectural Diagrams
2.1 What are Sectional Diagrams
Sectional diagrams provide a vertical cut ‘slice’ through a building, revealing its internal spatial relationships and structural elements. The cut line of sectional diagrams can also extend beyond the proposal to include the topography and neighbouring buildings.
2.2 Use Cases for Sectional Diagram
Architects use sectional diagrams to convey how various levels of space interact in a vertical ‘sliced’ view, this method of architectural diagram aids in the understanding of a building's three-dimensional form.
2.3 Practical Examples of Sectional Diagram
We can observe the use of sectional diagrams in these example architectural portfolio pages, showcasing the internal spaces and structure.
3. Axonometric Architectural Diagram
3.1 What are Axonometric Architectural Diagrams
Axonometric diagrams are effective in showcasing an overall design proposal as they are three-dimensional representations without any perspective distortion. This 3D projection allows all elements of a proposal to be illustrated in full scale.
3.2 3D Representation and Visual Clarity
Architects utilise axonometric diagrams to illustrate complex spatial relationships and structures, providing a coherent and detailed depiction of a design.
3.3 Common Uses in Architecture
Axonometric diagrams are commonly employed in the final stages of design to present detailed construction and spatial views as well as large contextual aerial views.
4. Isometric Architectural Diagram
4.1 Isometric Diagram Explained
Similar to axonometric diagrams, isometric diagrams are a three-dimensional view of equal scale along all three axes with no perspective distortion.
4.2 Comparisons with Axonometric Diagram
While similar to axonometric diagrams, isometric diagrams can offer a different visual projection to emphasise certain design features.
4.3 Design Considerations
Isometric diagrams are a popular architectural diagram in design presentations, as they show technical representation skills.
5. Exploded Axonometric / Isometric Architectural Diagram
5.1 Breaking Down Exploded Diagrams
Exploded axonometric/isometric diagrams literally ‘explode’ a design, exposing individual components in a hierarchal view.
5.2 Enhancing Understanding of Structural Elements
Architects use exploded diagrams to illustrate the relationships between different elements of a building.
5.3 Creative Applications in Architecture
This type of architectural diagram demonstrates strong visual representation skills as it is a technical drawing method.
They are useful for illustrating a breakdown of important architectural elements such as; spaces, circulation, routes, and zones for example.
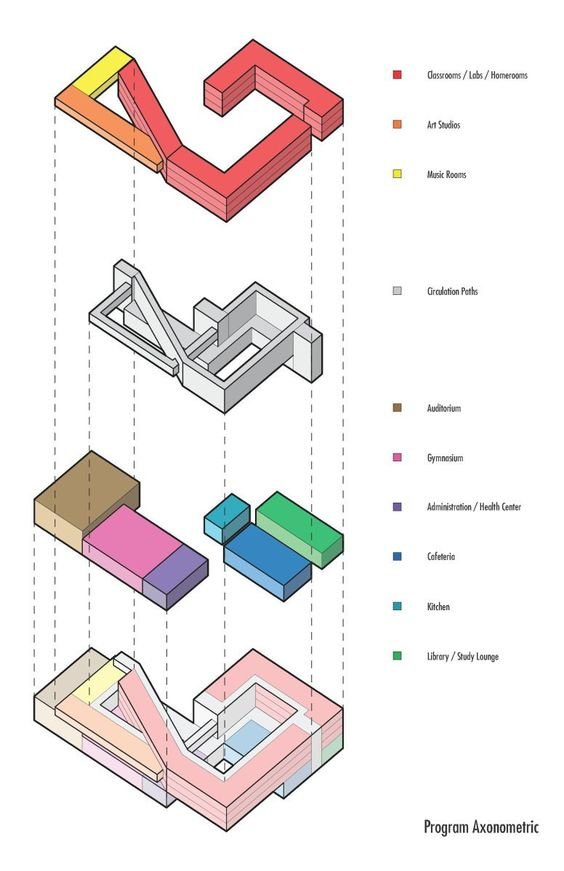
6. Programmatic Architectural Diagram
6.1 Defining Programmatic Diagrams
Programmatic architecture diagrams are a hybrid of architectural drawings and an infographic diagram. They are abstract diagrams illustrating characteristics of a design such as a breakdown of colour-coded zones.
6.2 Linking Design with Functional Requirements
Architects use programmatic diagrams to visualise practical and informational elements of the design that are usually brief requirements.
6.3 Examples of Programmatic Architectural Diagrams
Examples of programmatic architecture diagrams can be a great source of inspiration for your drawings.
7. Contextual Architectural Diagram
7.1 Contextual Diagrams in Architectural Planning
Contextual diagrams show the relationship between the proposed building with its surrounding environment, considering elements like landscape, neighbouring structures, and urban fabric.
7.2 Integration with Surrounding Environment
Architects use contextual diagrams to ensure that a design is well connected to the surrounding context and amenities.
7.3 Landscape Architecture and Urban Design
Contextual diagrams are important design aids in projects where the integration of architecture with the built or natural environment is paramount.
8. Architectural Circulation Diagrams
8.1 What are Architectural Circulation Diagrams
Circulation diagrams focus on optimising the flow of people and vehicles through internal and external spaces to ensure the efficiency of free-flowing movement. They are used to improve user experience and facilitate smooth movement.
8.2 Examples of Architectural Circulation Diagrams
Circulation diagrams vary based on scale, spatial requirements and surrounding landscape.
9. Structural Architectural Diagram
9.1 What are Structural Diagrams
Structural diagrams are used in the later stages of a project when the design is being refined. They illustrate a detailed representation of the structural and construction elements of the building.
10. Scaled Architectural Diagram
10.1 Understanding Scaled Diagrams
Scaled architectural diagrams illustrate the scale of the proposal in relation to the surrounding context and to a human scale.
10.2 Why Scaled Architectural Diagrams are Important.
Architects use scaled diagrams to ensure the spaces and architecture they are designing are proportionate and adequate to the spaces’ requirements.
11. Design Development Architectural Diagram
11.1. Significance in Design Development Diagrams
Design development diagrams capture the important narrative of the design process, illustrating the design development process and decision-making.
12. Building Phases Architectural Diagram
12.1 Visualising Design and Construction Stages
Architectural phases diagrams help stakeholders understand the sequential phase of the construction process, from groundwork to completion.
12.2 Client Communication through Phased Diagrams
Architects use phases diagrams to keep clients and other stakeholders informed about the construction process and time frames.
13. AI Generative Architectural Diagram
13.1 Exploring Generative Design in Architecture
AI Generative architectural diagrams are created with artificial intelligence to create innovative and unique design concepts.
13.2 AI and Computational Approaches
Architects need to embrace AI generative design as a tool to explore endless design possibilities, pushing the boundaries of creativity.
13.3 Future Trends and Possibilities
The integration of AI generative design could be a part of future architecture, most likely as an aid in concept design and then the design will be refined using traditional architecture skills and methods.
14. Spatial Architectural Diagram
14.1 What are Spatial Architectural Diagrams
Spatial Architectural diagrams visualise the relationship between spaces within an architectural project.
14.2 Why are Spatial Architectural Diagrams Important
Spatial Architectural diagrams are arguably the most important type of diagram to be used by architects, as they are imperative to aid the design of quality spaces.
15. Volumetric Architectural Diagrams
15.1 What are Volumetric Architectural Diagrams
Volumetric diagrams visualise the mass and spatial relationships of a design.
15.2 Visualising Mass and Space Relationships
Architects use volumetric diagrams to convey the proportion of 3D mass and voids within a proposal. They are also useful for visualising the impact of the 3D mass on the surrounding context.
Conclusion
In conclusion, by mastering these architectural diagram methods you will be able to design to the best of your abilities and communicate your design ideas and final projects successfully, not to mention you will showcase your advanced graphic and representational skills.
Found this guide helpful? Our eBook ‘A Graphic Guide to Architecture Concepts’ is packed with over 60 architectural diagrams and illustrations!
What else would you include for ‘Understanding Architectural Diagrams’?
We’d love to hear your thoughts… comment below!